Home
Categories
Dictionary
Glossary
Download
Project Details
Changes Log
What Links Here
FAQ
License
Distributing data structures as objects
1 Use case
2 Data objects
3 Detecting an underlying instance change
4 Sharing objects between applications
5 See also
2 Data objects
3 Detecting an underlying instance change
4 Sharing objects between applications
5 See also
In some cases, you have a service containing complex data structures, and you need to use them in several modules, but you don't want to decode the structure for each module.
It is possible to convert the data structures to Java objects and deliver it in another service as objects. However, you must be aware that these objects can of course only be used by Java modules.
Suppose that we have a
We want to use this array of waypoints in several Java modules, but we don't want to decode it in each module. We can define a
The user modules will be notified from the
For the previous example you can perform:
If you pass along object Types between different applications, you must reference the jar file which contain the underlying class definition in the
For example, suppose the following service definition:
You need to use the following definition instead:
It is possible to convert the data structures to Java objects and deliver it in another service as objects. However, you must be aware that these objects can of course only be used by Java modules.
Use case
Main Article: Data objects tutorial
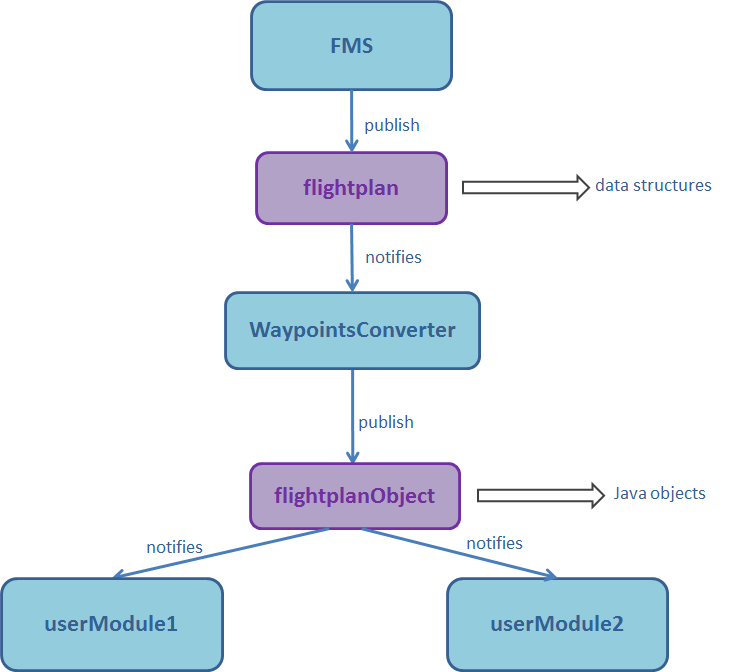
Suppose that we have a
FMS module sending a flightplan service which contains an array of waypoints. Each waypoint is a structure with a latitude and longitude.We want to use this array of waypoints in several Java modules, but we don't want to decode it in each module. We can define a
WaypointsConverter module which will be notified from the waypoints service, will decode the array of waypoints, and send a waypointsObject service which will not contain an array of waypoints but a Waypoints Java object.The user modules will be notified from the
flightplanObject service reception, and will only have to get the Waypoints object from the received data rather than having to make the decoding.
Data objects
The type objectType is used for elements which hold a Java object. For example, if the following service definition:<publish name="context" > <data name="waypoint" type="waypointObj" /> </publish>And the associated type definition:
<types> <objectType name="waypointObj" class="org.da.Waypoint" /> </types>Then
waypoint will be an instance of the org.da.Waypoint class. For example, if you want to set the data value before the service invocation, you can just code:Waypoint wpt = new Waypoint(); wpt.setPosition(latitude, longitude); wpt.setName("TTO"); Data data = service.getData("waypoint"); data.setValue(wpt);And when notified, you can just perform:
public void receive(Service service) { Data data = service.getData("waypoint"); Waypoint wpt = (Waypoint)data.getValue(); }
Detecting an underlying instance change
Datas of theobjectType type will be instances of the Data.Obj class. This class has a Data.Obj.isInstanceChanged() method showing if the underlying instance has changed since the last notification (meaning that it is not the same instance)For the previous example you can perform:
public class TheModule { Waypoint wpt = null; public void receive(Service service) { Data.Obj data = (Data.Obj)service.getData("waypoint"); if (data.isInstanceChanged()) { wpt = (Waypoint)data.getValue(); } } }
Sharing objects between applications
Main Article: Sharing libraries between applications
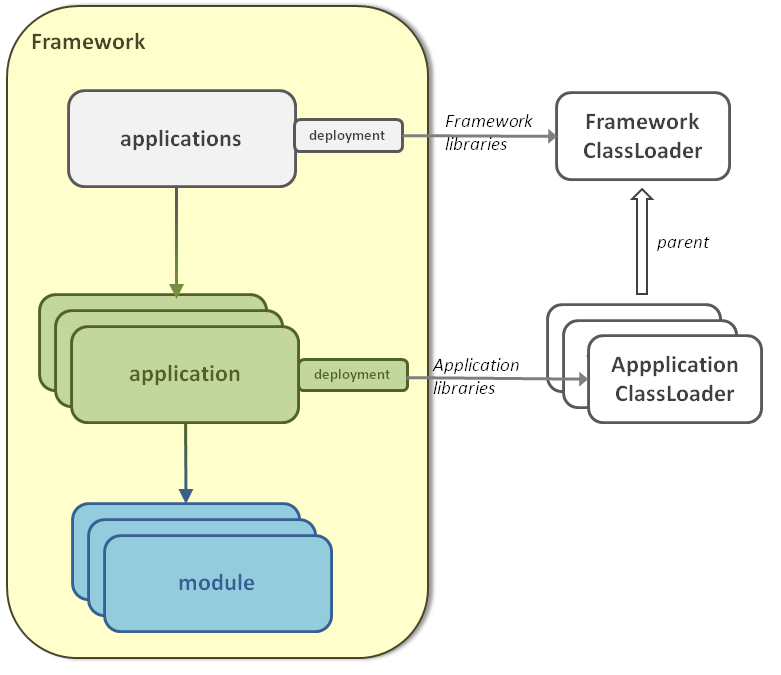
If you pass along object Types between different applications, you must reference the jar file which contain the underlying class definition in the
applications deployment libraries rather than reference it in each application deployment. 
For example, suppose the following service definition:
<publish name="context" > <data name="waypoint" type="waypointObj" /> </publish>And the associated type definition:
<types> <objectType name="waypointObj" class="org.da.Waypoint" /> </types>if the
waypoints.jar library contains the org.da.Waypoint definition, this applications configuration will not work:<applications> <application name="FMS"> <deployment> <lib url="FMS.jar" /> <lib url="waypoints.jar" /> </deployment> ... </application> <application name="WaypointsConverter"> <deployment> <lib url="WaypointsConverter.jar" /> <lib url="waypoints.jar" /> </deployment> ... </application> </applications>You will have the following exception when initializing the framework:
You need to use the following definition instead:
<applications> <deployment> <lib url="waypoints.jar" /> </deployment> <application name="FMS"> <deployment> <lib url="FMS.jar" /> </deployment> ... </application> <application name="WaypointsConverter"> <deployment> <lib url="WaypointsConverter.jar" /> </deployment> ... </application> </applications>
See also
- object types: This article explains the concept of data types
×
![]()
Categories: concepts | development