Home
Categories
Dictionary
Glossary
Download
Project Details
Changes Log
What Links Here
FAQ
License
Communication Protocol
1 Communication sequence
2 Structure of a message
2.1 Nominal messages
2.2 Exceptions messages
3 Error types
4 Service content
4.1 Simple types
4.2 Array types
4.3 Structure types
4.4 Union types
4.5 Map types
5 Time stamp
6 Notes
7 See also
2 Structure of a message
2.1 Nominal messages
2.2 Exceptions messages
3 Error types
4 Service content
4.1 Simple types
4.2 Array types
4.3 Structure types
4.4 Union types
4.5 Map types
5 Time stamp
6 Notes
7 See also
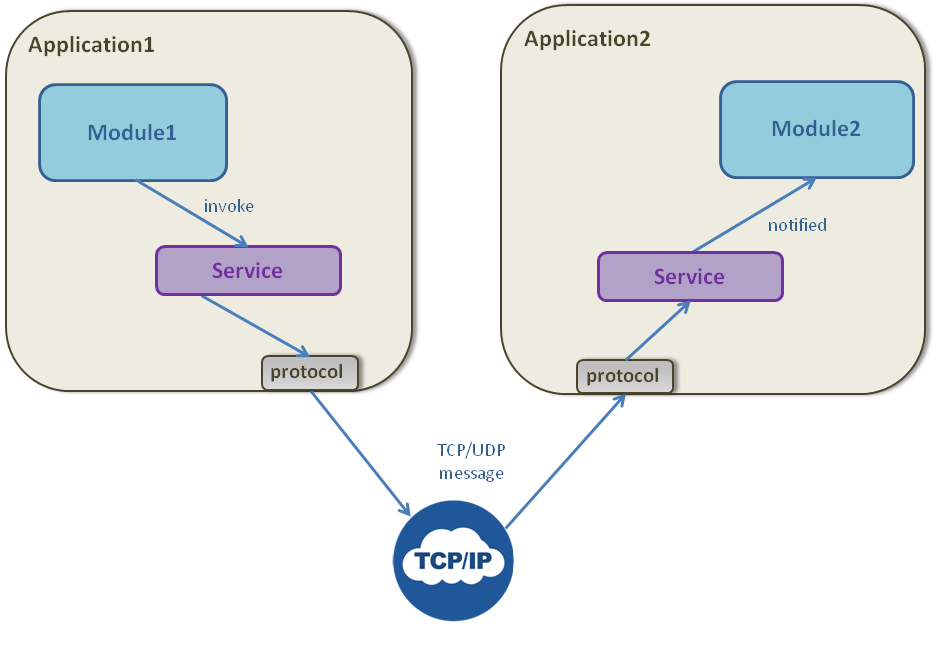
Invoking services can be performed through the UDP or TCP protocol. This article explains the structure and the content of the data used for this invocation.
How the datas are serialized depends on their type. To serialize a complex type, the framework will serialize each element composing the type.
Communication sequence
The sequence of communication for a Service invocation through TCP or UDP is as follows:- The provider module calls the
invoke()method for the Service - The framework which controls the provider module defer the invocation to the implementation of the protocol protocol which is used for the subscriber module
- The framework which controls the subscriber module receives the TCP or UDP message
- The framework which controls the subscriber module notifies this module

Structure of a message
There are two types of messages:- Nominal messages which are sent normally for a Service invocation
- Exception messages which are sent when a Module emits an error
Nominal messages
A nominal message has the following structure:| Size in bits | Data Type | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 32 | int | MAGIC keyword[1]
The MAGIC keyword value is
0xDA666 |
| 64 | long | Service ID |
| 8 or 16[2]
Size depends on the value of the
charAs8Bits property |
char[3]
If
charAs8Bits is true, this is a C-type char on 8 bits, encoded on 1 byte, which is equivalent to a Java byte. A Java char would have been encoded on 2 bytes, so on 16 bits. Because of that, the regular encoding way in Java for a char value would be for example with Netty:
byte b = (byte)charValue; byteBuf.writeByte(b);If charAs8Bits is false, this is a Java-type char on 16 bits, encoded on 2 bytes. |
INVOKE keyword[4]
The INVOKE keyword value is
0x01 |
| 64 | long | Time stamp (See Time stamp) |
| 64 | long | Request ID (different from 0 if the invocation corresponds to a request) |
| N/A | N/A | Service content (see Service content) |
Exceptions messages
An exception message has the following structure:| Size in bits | Data Type | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 32 | int | MAGIC keyword[1]
The MAGIC keyword value is
0xDA666 |
| 64 | long | Service ID |
| 8 or 16[2]
Size depends on the value of the
charAs8Bits property |
char[3]
If
charAs8Bits is true, this is a C-type char on 8 bits, encoded on 1 byte, which is equivalent to a Java byte. A Java char would have been encoded on 2 bytes, so on 16 bits. Because of that, the regular encoding way in Java for a char value would be for example with Netty:
byte b = (byte)charValue; byteBuf.writeByte(b);If charAs8Bits is false, this is a Java-type char on 16 bits, encoded on 2 bytes. |
EXCEPTION keyword[5]
The EXCEPTION keyword value is
0x04 |
| 8 or 16[2]
Size depends on the value of the
charAs8Bits property |
char[3]
If
charAs8Bits is true, this is a C-type char on 8 bits, encoded on 1 byte, which is equivalent to a Java byte. A Java char would have been encoded on 2 bytes, so on 16 bits. Because of that, the regular encoding way in Java for a char value would be for example with Netty:
byte b = (byte)charValue; byteBuf.writeByte(b);If charAs8Bits is false, this is a Java-type char on 16 bits, encoded on 2 bytes. |
error type (see error types) |
| 64 | long | Time stamp (See Time stamp) |
| 64 | long | Request ID (different from 0 if the error corresponds to an invalid request) |
Error types
The supported error types are:| Name | Value | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| ERROR_NO_ERROR | 0x00 |
No error, should never be set to this value |
| ERROR_TIMEOUT | 0x01 |
Timeout error, normally not sent by the Network |
| ERROR_INVALID_REQUEST | 0x02 |
Invalid request error |
Service content
The serializarion of the Service is the list of datas defined for the Service in the order in which they are defined in their XML configuration. For example, for the following Service:<publish name="position" > <data name="latitude" type="float" /> <data name="longitude" type="float" /> <data name="altitude" type="float" /> </publish>The order in which the datas will be sent will be:
- latitude
- longitude
- altitude
How the datas are serialized depends on their type. To serialize a complex type, the framework will serialize each element composing the type.
Simple types
Simple types are serialized directly:| Data Type | Size in bits | Content |
|---|---|---|
| int enum |
32 | signed int value |
| short | 16 | signed short value |
| long | 64 | signed long value |
| byte | 8 | byte value |
| char | 8 or 16[2]
Size depends on the value of the
charAs8Bits property |
signed char value[3]
If
charAs8Bits is true, this is a C-type char on 8 bits, encoded on 1 byte, which is equivalent to a Java byte. A Java char would have been encoded on 2 bytes, so on 16 bits. Because of that, the regular encoding way in Java for a char value would be for example with Netty:
byte b = (byte)charValue; byteBuf.writeByte(b);If charAs8Bits is false, this is a Java-type char on 16 bits, encoded on 2 bytes. |
| float | 32 | IEEE float value |
| double | 64 | IEEE double value |
| boolean nil[6] nil elements will always have the 0x00 (false) value |
8 | 0x00 (false) or 0x01 (true) |
| string | 32 + {8+} or 32 + {16+}[2]
Size depends on the value of the
charAs8Bits property |
String length: int, characters: array of chars[7]
There is no \0 char for the end of the String
[3]
If
charAs8Bits is true, this is a C-type char on 8 bits, encoded on 1 byte, which is equivalent to a Java byte. A Java char would have been encoded on 2 bytes, so on 16 bits. Because of that, the regular encoding way in Java for a char value would be for example with Netty:
byte b = (byte)charValue; byteBuf.writeByte(b);If charAs8Bits is false, this is a Java-type char on 16 bits, encoded on 2 bytes. |
Array types
| Data Type | Size in bits | Content |
|---|---|---|
| int | 32 | array size |
| N/A | N/A | {value for each element in the array} |
Structure types
| Data Type | Size in bits | Content |
|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A | {value for each field in the structure} (in the order of their definition) |
Union types
| Data Type | Size in bits | Content |
|---|---|---|
| int | 32 | Union variant |
| N/A | N/A | value for the current member of the Union (corresponding to the variant) |
Map types
| Data Type | Size in bits | Content |
|---|---|---|
| int | 32 | Map size |
| N/A | N/A | {value for each key, value for each value} |
Time stamp
TheTime stamp value allows specifies the time stamp value for the Service (see Java modules service interface). Notes
- ^ [1] [2] The MAGIC keyword value is
0xDA666 - ^ [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] Size depends on the value of the
charAs8Bitsproperty - ^ [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] If
charAs8Bitsis true, this is a C-type char on 8 bits, encoded on 1 byte, which is equivalent to a Java byte. A Java char would have been encoded on 2 bytes, so on 16 bits. Because of that, the regular encoding way in Java for a char value would be for example with Netty:byte b = (byte)charValue; byteBuf.writeByte(b);
IfcharAs8Bitsis false, this is a Java-type char on 16 bits, encoded on 2 bytes. - ^ The INVOKE keyword value is
0x01 - ^ The EXCEPTION keyword value is
0x04 - ^
nilelements will always have the0x00(false) value - ^ There is no \0 char for the end of the String
See also
- Framework deployment: This article presents the framework deployment
- Network communication: This article explains how the network communication between Applications is defined
×
![]()
Categories: config